RESTRICTIVE FIREWALLS
 The most common cause is that one or more session participants is trying to use FarPlay on a network with an especially restrictive firewall (example: a university campus or workplace network). The steps on this page typically solve these problems.
If you’re a teacher, port forwarding will help you reach the widest range of students (including students on university campuses).
The most common cause is that one or more session participants is trying to use FarPlay on a network with an especially restrictive firewall (example: a university campus or workplace network). The steps on this page typically solve these problems.
If you’re a teacher, port forwarding will help you reach the widest range of students (including students on university campuses). Using forwarded ports with FarPlay
If you’re having trouble connecting from home to another FarPlay user (particularly if the other user is on a university campus or corporate network), it might help to configure your copy of FarPlay to use forwarded ports.
Open your router settings 
| Router from | Router address |
|---|---|
| Verizon FiOS | http://myfiosgateway.com or http://192.168.1.1 |
| Comcast Xfinity | http://10.0.0.1 |
| Optimum | http://router.optimum.net |
| AT&T | http://192.168.1.254 |
| Spectrum | http://192.168.0.1 |
| TP-Link | http://192.168.0.1 or http://192.168.1.1 |
- Use a web browser to open your router’s webpage. The table at the right provides common router addresses. If you can’t find the address of your router using this table, you can look for the address of your router by navigating through system settings to a page of information for your Ethernet adapter and then finding the address labeled “Default IPv4 Gateway” or “Router”. Configuration webpages vary from router to router. The screenshots below were taken from a Verizon FiOS router.
- Log in with your router username and password, if needed.
Assign a Static IP Address to your computer
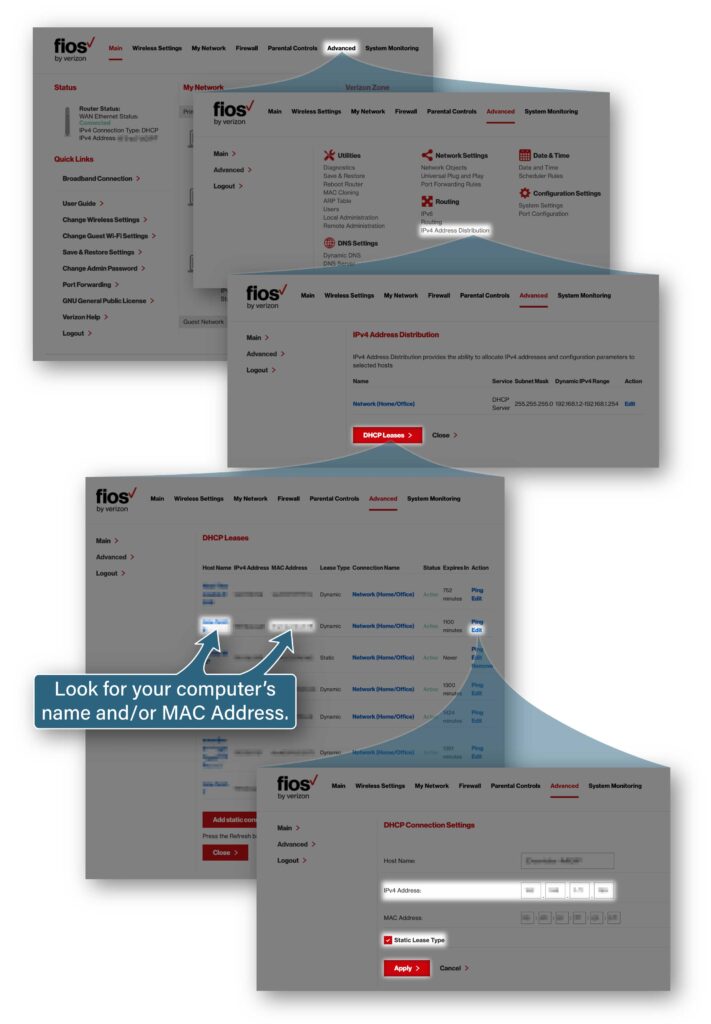
- Find the list of devices on your home network and their private IP addresses. For example, on some Verizon FiOS routers, click Advanced, look for the Routing section, click IPv4 Address Distribution, and then click DHCP Leases.
- Find the entry for the computer you are running FarPlay on (you can look for a descriptive host name and/or your computer’s MAC Address).
- Open the private IP address settings for your computer. On a Verizon FiOS router, you would click “Edit.”
- Write down the private IPv4 Address of your computer.
- Make sure the checkbox that makes your computer use a Static Private IP Address is checked (on a Verizon FiOS router, the checkbox might be labeled “Static Lease Type”).
- Confirm settings (on a Verizon FiOS router, click “Apply”).
Port forward your computer
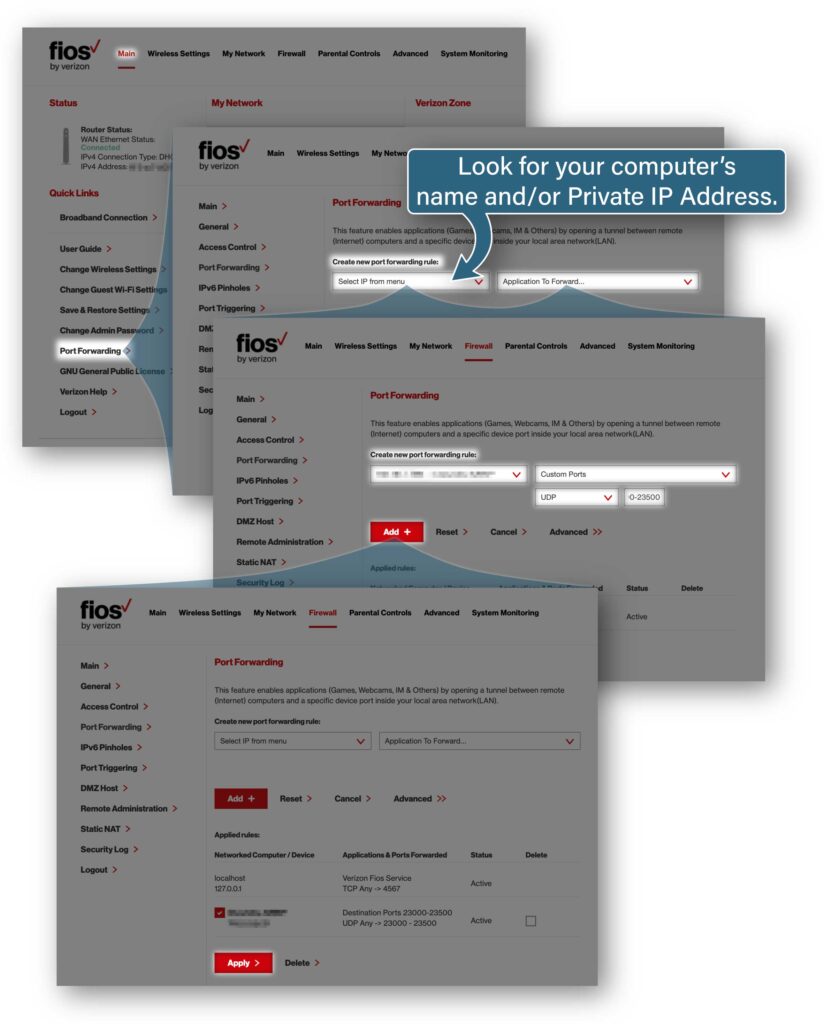
- Open the list of forwarded ports on your router. For example, on some Verizon FiOS routers, click Main, look in the list of Quick Links, and click Port Forwarding.
- Create a new rule using the private IP address you wrote down for your computer.
- Where the router asks what kind of ports to forward, choose UDP and enter a hyphenated port range (example: 60000-60100).
- Write down the port range you entered.
- Accept the new port forwarding rule (on a Verizon FiOS router, click “Add +” and then Apply).
Copy port numbers into FarPlay
- Open the FarPlay menu, choose Preferences to bring up the Preferences control panel. Navigate to the “Advanced” tab.
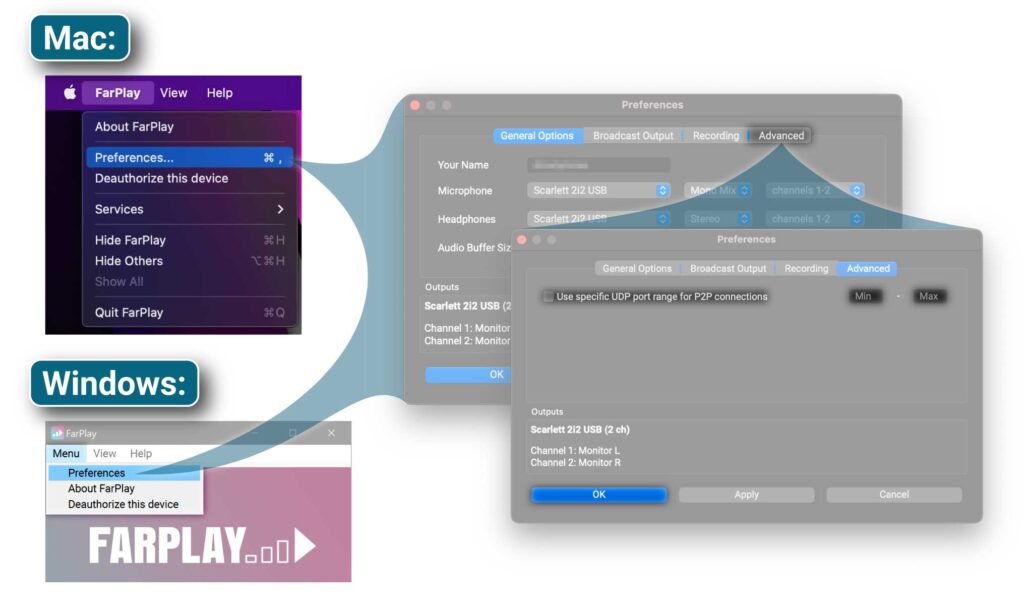
- Checkmark “Use specific UDP port range for P2P connections.”
- Enter the range of ports you forwarded in your router settings using the entries labeled “Min” (left box) and “Max” (right box).
- Click OK.
- Try connecting again!
Connecting from Campus or a Workplace
If you’re having trouble connecting on FarPlay from a computer on a campus or workplace network, the FarPlay Team is eager to help. Use our forum, and we’ll respond as soon as we can!
If you’d like to point your IT administrator to our network requirements, they are provided below.
If your IT administrator would like to meet to discuss network requirements, we invite them to email us at support@farplay.io.
| FarPlay needs … | FarPlay has difficulty with … | FarPlay works with … |
|---|---|---|
TCP ConnectivityCurrently, FarPlay needs to connect over TCP to ports 443, 3400–3650, and 6727 on our server at connect.farplay.io.⚠ Enabling all TCP traffic to the farplay.io domain is recommended for guaranteeing reliable operation in the future. UDP P2P Connectivity
|
A well known problem is having Symmetric NAT at one of the ends of an attempted connection. If one user has no choice but to connect using a network that uses Symmetric NAT (common for workplace and campus networks), the other end will need to try to use forwarded ports, as described above. | Common (not symmetric) NATs and connection-tracking UDP firewalls (which allow UDP responses, but block random incoming UDP packets) are not problems for FarPlay, which should work flawlessly with such network configurations. |
You can ask your IT administrator whether they can help you with any of the following.
- Can we turn off packet inspection for my computer?
- Can we put my computer on a VLAN to avoid on-campus traffic?
- Does our campus have a subnet for gaming? Can we put my computer on that subnet?
- Can we put my computer in a DMZ just for the limited duration of an event?
- Can we set up 1:1 NAT for my computer?
When asking questions 4 and 5, mention that FarPlay can be configured to use only a limited range of ports for UDP communication.